Autonomic Nervous System Balance
We established in part 1 that due the many years of nutritional research working on the front line with many patients Dr William Donald Kelley and William Woolcott devised an ingenious methodology to ascertain the correct diets and supplementation to match an individual’s metabolism.
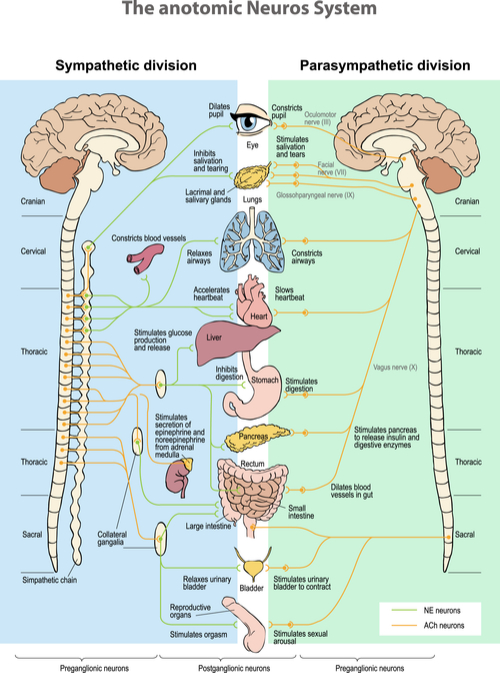
By drawing upon such classic works from Francis Pottenger, Ernst Gellhorn, and George Watson it was the Autonomic nervous system (ANS) and cellular oxidation that both held the key to their nutritional customization.
From this extensive empirical work it identified that individuals who had ANS sympathetic dominance were more suited to a plant based diet consuming complex carbohydrates, yielding the most Vitamin C and Beta carotene, and thrived on essential vitamin /Mineral nutrients such as Thiamin, Riboflavin, Pyridoxine, Biotin, Vitamin D,K, Niacin magnesium, chromium, manganese and Potassium.Folate. While individuals who had an ANS Parasympathetic dominance were more suited to a more meat based, high protein diet and thrived on essential vitamin/mineral nutrients that included Vitamin B12, A, Pantothenic acid, E, Calcium, Phosphorous, Iron, Selenium and Sodium, and Niacin. The third category were the balanced individuals could eat a ‘smorgasbord’ type of diet.

Alternative Dominance Testing
Although Kelley spent a few years of his life determining which food and what nutrients to balance the body’s chemistry when the autonomic nervous system, that drives the whole body, is out of balance.
Using a very sophisticated testing regimen involving 3200 questions, he was able to determine ANS dominance which was the key to which branch needed to be suppressed and what branch needed to be enhanced to achieve chemical balance and metabolic equilibrium.
Today testing for dominance is made easier and one test involves taking niacin which has alkaline tendencies toward the body. By ingesting 50 mg of niacin (not niacinamide) on an empty stomach, and the skin turns red, irritated and begins to feel hot within say 1/2 hour then it is more than likely the individual is Parasympathetic dominant (niacin will aggravate an already alkaline Para-dominant person).
A person that does not feel anything suggests Sympathetic dominance. However, feeling warmer and a having good facial color suggests a balanced metabolism. Alternatively, by taking 8g of Vitamin C (which has an alkaline effect on the body the same way niacin does) for 3 days and after that time the person feels depressed, fatigued, lethargic and irritable and in the case of a female, vaginal irritability, then that person is Parasympathetic dominant.
On the other hand if the person feels energetic; quite the opposite, then the person is Sympathetic dominant. No change suggests a balanced metabolism.
However Chiropractors can conduct a heart variability test also to detect ANS dominance
Cellular Oxidation Balance
William Wolcott went a stage further by identifying the cellular oxidation of each cell that also had an influence over metabolic balance, citing that some individuals could burn nutrients fast which he referred to as the ‘fast oxidizers’, while others had a slower oxidation rate which he referred to as ‘slow oxidizers’ and a third category who were mixed.
This meant that the fast oxidizers needed fuel that would need a slower burn rate so as they would not run out of energy, like meat protein and fat. While the slower oxidizers needed fuel that required less metabolic effort such as carbohydrates, grains and seeds.

ANS and Cellular Oxidation
This results in 4 permutations:
- Parasympathetic Dominant, Slow Oxidizers
- Parasympathetic Dominant, Fast Oxidizers
- Sympathetic Dominant Slow Oxidizers
- Sympathetic Dominant Fast Oxidizers
The fact that Parasympathetic dominance need an acid base meat eating type diet and Fast oxidizers need the same type of diet then we have a ‘nutritional match’.
This applies to Sympathetic dominance and Slow Oxidisers. It is the Parasympathetics/slow oxidisers and Sympathetics/fast oxidizers that need closer attention, since you have a nutritional conflict.
Although ANS and cellular oxidation held the key to customizing a diet that matched an individual’s metabolism, there were still other physiological processes to consider to fine tune the proposed dietary protocol.
According to the extensive research on metabolic typing by William Wolcott, he believed that Acid/Alkalinity balance is dependent upon at least 7 homeostatic regulators:
- ANS (Sympathetic dominance =Acid, Parasympathetic dominance=Alkaline)
- Oxidation (Fast = acid, Slow=alkaline)
- Catabolic (Tissue =alkaline, system=acid), Anabolic (Tissue=acid, system=alkaline)
- Electrolyte/fluid balance: Precisely regulated by 7 major electrolytes but in terms of PH Chloride and Bicarbonate are the electrolytes the main regulators.
- Endocrine: Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, gonads) that regulate acid/alkaline minerals.
- Respiration: When oxygen is inhaled the body converts it into Carbon dioxide (CO2) and when exhaled the carbon dioxide is removed from the body. Carbon dioxide is a respiratory acid, so inadequate breathing can cause this respiratory acid to build up in the tissues. This additional CO2 combines with water to form Carbonic acid that increases blood PH.
- Acid/alkaline ‘ash’ from food
Dr. Guy Schenker who specialises in clinical nutrition has identified 6 other possible imbalances namely:
- Metabolic acidosis
- Metabolic alkalosis
- Respiratory acidosis
- Respiratory alkalosis
- Potassium excess acidosis
- Potassium depletion alkalosis
Catabolic/Anabolic Balance

The cells within our body adjust their membranes depending of the time of day.
In the morning our cells are more receptive to nutrients and permeable allowing a greater exchange of energy. This is referred to as Catabolism which is a normal process during metabolism where larger ingested substances are broken down into much smaller particles in order to drive the cell’s energy needs (i.e feeds the oxidation process).
When the cells are in a catabolic state during the day the cell membranes are permeable allowing nutrients to enter and exit with ease. Catabolism is our ANS sympathetic equivalent, whereas the opposite metabolic state is Anabolism which is our rest and rebuild process equivalent to the ANS parasympathetic state.
Dr. Emanuel Revici who researched these natural processes found that sick individuals were stuck in a state of Catabolism or Anabolism.
Getting stuck in a Catabolic state causes the body to grind to a halt with exhaustion, while energy stores get depleted and excessive metabolite waste is produced.
A state of Anabolic inertia is moving closer to anaerobic fermentation where anabolic cells are starved of oxygen.
Generally, during the night while the body is at rest the cell membranes restrict access to nutrients, but if this anabolic state continues through the day, overtime, the cells become starved of fuel and subsequently cannot generate energy.
Either state is caused by an nutrient deficiency or nutrient imbalance, specifically an imbalance of essential fats that the cell membrane is made of.
Cell membranes are bi-lipid (2 substances saturated fat and cholesterol ) and if nutrient deficient, their membranes become less permeable prohibiting vital nutrients to enter the cell leading to Catabolic imbalance.
Catabolic imbalance signals the host with the one or more of the following ‘symptoms’:
- Migraine headaches,
- Chronic diarrhea,
- Hair loss,
- Muscle loss and pain,
- Low body temperature,
- Oliguria. (Decreased production of urine)
If your body deteriorates to this level of imbalance it is advisable to immediately start supplementing with the 90 essential nutrients 16 vitamins,12 amino acids, 60 minerals and 3 essential fatty acids, in a whole food complex (no supplement pills) and to increase the intake of coconut oil and butter. This applies to both Catabolic and Anabolic imbalance.
Anabolic Imbalance

As you are probably aware weightlifters take Anabolic steroids to build muscle, enhancing the normal Anabolic process to gain an advantage over their competition. However, if you happen to be in a state of Anabolic imbalance you might experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Constipation
- Tachycardia ( an abnormal rapid heart beat)
- Anxiety/panic attacks
- Polyuria (frequent urination)
- Problems with waking up
- Viral problems
- UTI (Urinary tract and/or bladder infection)
PH -Acidity/Alkalinity Balance

The rate of oxidation does affect Acidity/Alkalinity of the body since fast oxidation produces excess lactic acid as a metabolite within an environment that is typically low in calcium and magnesium needed to neutralize waste acids.
However, if the individual is healthy, they can generally tolerate these conditions.
Furthermore, in slow oxidation the production of these acidic metabolites is less, however there is a tendency for bowel toxins to build up with slow liver function and reduced bile secretion in some slow oxidisers.
Although physiological acidity/alkalinity is more widespread and is affected by other biological functions as we will investigate in Part 3.

“He bringeth forth grass for the cattle: and green herb for the service of men; That he may bring food out of the earth,and wine that maketh glad the heart of man; and oil to make him a cheerful countenance,and bread to strengthen man’s heart. The trees of the Lord also are full of sap;even the cedars of Libanus which he hath planted.”
Psalm 104 v.18
Check out the Previous Article in this series:
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/metabolic-typing-part-1/
References/Acknowledgments:
- The Metabolic typing diet William Wolcott & Trish Fahey (2000)
- What is a Catabolic state Fitday website
- Cell membrane physiology Biosynergypro website
- Nutrition and disease Distance Healer website
Author: Eric Malouin